Learning Goals
At the end of this Tutorial, you will be able to:
- Understand how spreadsheet data maps to arrays of objects
- Display structured data in the browser console
Arrays of objects
Arrays of objects are a very common data structure in JavaScript. They are typically used to work with collections of related data such as lists of:
- users
- products
- social media posts
- transaction records
Each item in the array is an object that follows the usual key-value property structure.
Consider the stylesheet-style table of three products below.
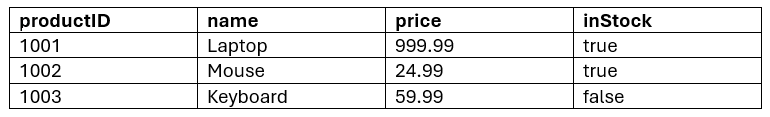
In JavaScript, you can represent this entire dataset as an array (with square brackets []).
Each record row is an object (with curly braces {}).
Each object has the same keys (matching the spreadsheet columns).
As in regular arrays, the items (objects) are separated by commas ,.
Objects and arrays: a review
In the previous Introduction to objects and Introduction to arrays Tutorials, you learnt the following:
- Object (Lots of data about one thing): A collection of properties with two parts: a key (such as firstName) and a value (such as Luis).
Each property value can be accessed with the object name, a dot ., and the key name (such as objUser.firstName).

- Array (Lots of things): An ordered list of items of the same data type, such as strings or numbers. A comma , character separates the items in the list.
Each array item can be accessed by its index position inside square brackets [n], beginning at zero. For example, arrEmployeeIDs[3] would be the fourth item in the array, 1237.

Working with arrays of objects
Copy this code to your workfile:
// Creating an array of objects
const arrProducts = [
{
productID: 1001,
name: "Laptop",
price: 999.99,
inStock: true
},
{
productID: 1002,
name: "Mouse",
price: 24.99,
inStock: true
},
{
productID: 1003,
name: "Keyboard",
price: 59.99,
inStock: false
}
];
console.log(arrProducts);
Each item in the array is an object that follows the same property structure, making it easy to organise and process data.
The general form of an array of objects is below.

For convenience, the objects in an array are often typed on a single line. Copy the example below.
// Creating an array with objects on a single line
const arrUsers = [
{ firstName: "Alice", age: 25, city: "New York", isActive: true },
{ firstName: "Bob", age: 30, city: "Los Angeles", isActive: false },
{ firstName: "Charlie", age: 35, city: "Chicago", isActive: true }
];
console.log(arrUsers);
Displaying data from an array of objects
An important difference between a single object and objects in an array is that objects in an array do not have a name.
For an individual object, you access a property value by entering the object name (such as objLaptop) and the property key (such as price). See below.
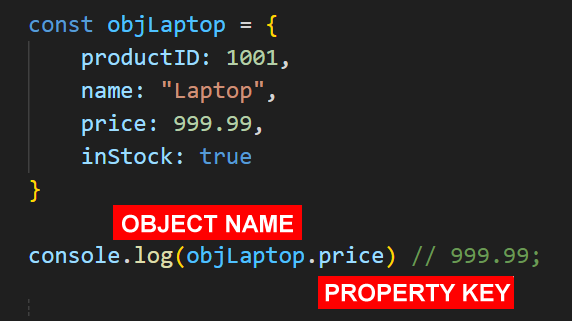
However, for objects in an array, you instead access data from a particular object by its index position and its property key.
Copy the code below that displays selected property values from your two arrays of objects.
// Displaying some data from the arrProducts array of objects
console.log(`ID of product 0: ${arrProducts[0].productID}`); // 1001
console.log(`Name of product 1: ${arrProducts[1].name}`); // Mouse
console.log(`Price of product 2: ${arrProducts[2].price}`); // 59.99
// Accessing the first user's first name property
console.log(`First user: ${arrUsers[0].firstName}`);
// Accessing the second user's age property
console.log(`Second user's age: ${arrUsers[1].age}`);
// Checking if the third user is active
console.log(`Is the third user active? ${arrUsers[2].isActive}`);Looping through arrays of objects
Arrays may have many hundreds of objects, each with lots of properties. So it is impractical to enter a line of code to display each property value of every object.
The solution is to use a .forEach() loop on each object in the array.
The general syntax for this loop is as shown below.

Copy the code below.
// Loop through arrProducts
arrProducts.forEach(product => {
console.log("Product Details:");
console.log(`ID: ${product.productID}`);
console.log(`Name: ${product.name}`);
console.log(`Price: €${product.price}`);
console.log(`In Stock: ${product.inStock}`);
console.log("---------------"); // Separator between products
});Copy this code to output data from the arrUsers array of objects.
// Loop through arrUsers
arrUsers.forEach(user => {
console.log("User Details:");
console.log(`First Name: ${user.firstName}`);
console.log(`Age: ${user.age}`);
console.log(`City: ${user.city}`);
console.log(`Active?: ${user.isActive}`);
console.log("**************"); // Separator between users
});Reformatting the output from an array of objects
With a .forEach() loop, you can perform any valid operation on the items in an array. For example, you can format the output in a more readable way. You can also display new outputs based on operations on the retrieved data.
Outputting string values
Sometimes, string values in the array of objects may contain extra spaces before or after the actual text. You could use the .trim() method to remove these extra spaces from the output of the arrProducts array.
// Removes extra spaces before/after name
console.log(`Name: ${product.name.trim()}`);
You could use the .toUpperCase() method to display a product's name in capital letters.
// Remove extra spaces before/after name
console.log(`Name: ${product.name.trim().toUpperCase()}`); Outputting numeric values
To display a discounted price along with the price retrieved from the array, you could add a helper function to your code such as the following.
// Helper function to round to 2 decimal places
function roundMoney(amount) {
return Math.round(amount * 100) / 100;
}You can then call this helper function inside the loop as follows.
// Calculating and displaying a discounted price
const discountedPrice = roundMoney(product.price * 0.9);
console.log(`Price: €${product.price}, Discounted Price: €${discountedPrice}`);Note: Using the .toFixed(n) method for calculations is dangerous because it converts your number into a string (text), which breaks any future math you might want to do with that variable.
Outputting boolean values
To display a more user-friendly message based on a boolean property value (true or false), you could use an if...else statement to set a variable to a specific string based on the boolean value.
// *** Alternative to true/false output ***
let stockStatus; // Variable to hold stock status
if (product.inStock) { // tests stock status
stockStatus = '✅ Currently Available'; // if test returns true
} else {
stockStatus = '❌ Out of Stock'; // if test returns false
}
console.log(`In Stock? ${stockStatus}`); // Outputs result
In modern JavaScript, a more common approach would be to use the ternary operator.
// *** Alternative to true/false output (ternary version) ***
const stockStatus = product.inStock
? '✅ Currently Available'
: '❌ Out of Stock';
console.log(`In Stock? ${stockStatus}`);
Try it yourself
In your workfile...
---
Create an array called arrBooks with at least four book objects. Each book object should have these properties:
- title (string)
- author (string)
- year (number)
- isRead (boolean)
You can use AI to generate the details.
Using a .forEach() loop, display each book's information in the console.
More learning resources
Tutorial Quiz
Tutorial Podcast
Sample AI prompts
I'm learning about arrays of objects in JavaScript. Could you help me understand them better by:
- Creating an example array of objects representing a playlist of songs
- Explaining how each part of the syntax works (brackets, braces, commas, etc.)
- Showing me how to access specific properties like the title of the second song
- Demonstrating how to loop through the array with .forEach() and display the data
- Please explain each step as if you're teaching a beginner.